home ![]() resource tuner tutorials
resource tuner tutorials ![]() how to...
how to...
How To Insert TrustInfo into Manifest to Identify the Application Security Requirements on Windows
Developers need a way to deploy the same build of the application on all Windows versions. However, a new feature of Windows, User Access Control (UAC) causes processes to run as standard user even if you are logged in with a user that is the member of the Administrators group.
If an application requires administrative privileges and needs to run elevated as an administrator, an application UAC manifest must be created and embedded. This manifest specifies the privilege level and instructs Windows to run the application with elevated permissions.
Resource Tuner offers a solution by allowing the patching of a pre-existing binary exe to inject the Require Administrator information. This ensures that the application runs as an Administrator on modern Windows versions, while still maintaining the same operational behavior as in Windows XP. Importantly, the modified exe should continue to function correctly on earlier versions of Windows.
“ I tried using mt.exe [from MS Visual Studio] to manifest my files. It worked on some but not on others. It seems your method of parsing the .EXE is more robust than the one that mt.exe uses. ” Brad Siegfried, |
Manifests were used in Windows XP to help application developers identify which versions of ComCtl DLLs the application was tested with. The Windows Vista application manifest schema has been enhanced with attributes that allow developers to mark their applications with a requested execution level. These new attributes indicate to the system that you have a legitimate administrative application. The system will automatically ask for approval from the user to launch the application with full privileges.
Microsoft has implemented an extension to the trustInfo section of the current Windows XP application manifest schema. The following is the format for this:
<requestedExecutionLevel
level="asInvoker|highestAvailable|requireAdministrator"
uiAccess="true|false"/>
where
level
- asInvoker — The application runs with the same token as the parent process.
- highestAvailable — The application runs with the highest privileges the current user can obtain.
- requireAdministrator — The application runs only for administrators and requires that the application be launched with the full token of an administrator.
If only a small number of features in an application will require administrative privileges (for example, an application needs to configure a firewall), the main process of the application must still be run as a standard user. The administrative features must be moved into a separate process that runs with administrative privileges.
uiAccess
- false — The application does not need to drive input to the UI of another window on the desktop. Applications that are not providing accessibility should set this flag to false. Applications that are required to drive input to other windows on the desktop (on-screen keyboard, for example) should set this value to true.
- true — The application is allowed to bypass UI protection levels to drive input to higher privilege windows on the desktop. This setting should only be used for UI Accessibility applications.
Applications that request uiAccess=true must have a valid, trusted digital signature to execute.
4 Easy Steps to Add the TrustInfo Section
1. Download Resource Tuner and open your file. In the Resource TreeView, locate and expand the Manifest folder. From there, select the Manifest resource you wish to edit.
Note: If your file lacks a manifest altogether, skip these steps and use the Manifest Wizard for creating and adding the manifest resource.
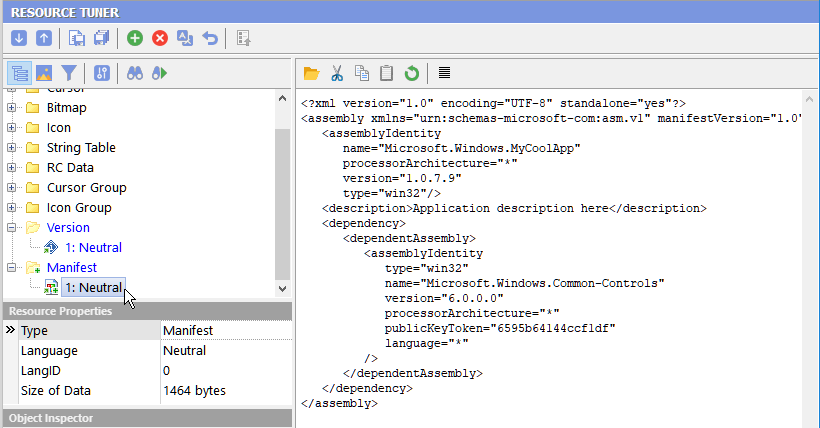
2. You will see the XML script. It may look something like this:
<assembly xmlns="urn:schemas-microsoft-com:asm.v1" manifestVersion="1.0">
<assemblyIdentity
name="Microsoft.Windows.MyCoolApp"
processorArchitecture="x86"
version="5.1.0.0"
type="win32"/>
<description>Application description here</description>
<dependency>
<dependentAssembly>
<assemblyIdentity
type="win32"
name="Microsoft.Windows.Common-Controls"
version="6.0.0.0"
processorArchitecture="x86"
publicKeyToken="6595b64144ccf1df"
language="*"
/>
</dependentAssembly>
</dependency>
</assembly>
It's important to verify that there is no trustInfo statement in the manifest at this stage.
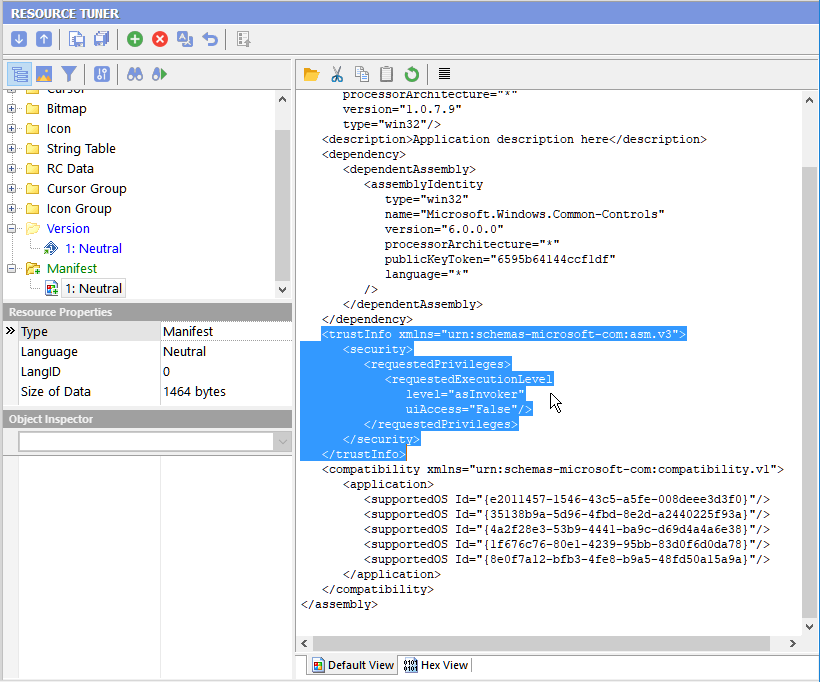
3. Now, let's insert the TrustInfo section into this manifest:
<!-- level can be "asInvoker", "highestAvailable", or "requireAdministrator" -->
<trustInfo xmlns="urn:schemas-microsoft-com:asm.v2">
<security>
<requestedPrivileges>
<requestedExecutionLevel
level="requireAdministrator"
uiAccess="false"/>
</requestedPrivileges>
</security>
</trustInfo>
4. Finally, select 'File' ![]() 'Save File' or use the [Ctrl+S] hotkey combination to save the changes made to the target file.
'Save File' or use the [Ctrl+S] hotkey combination to save the changes made to the target file.
Start Tuning Your Applications Now!

Resource Tuner runs on all versions of Windows, including 11, 10, 8, 7, and XP, and supports both 32-bit and 64-bit systems.